Propeller 101
As a motorsailer, Seeker will feature 3 sails as well as a diesel motor. Though we’d like to operate solely under wind power, there will be times where we will have to fire up the engine and depend upon the propeller to move us where we want to go.
So what do you need to know about propellers?
In a vessel that does not pull a net or dredge, of the energy that reaches the propeller:
35 percent is used to turn the propeller;
27 percent to overcome wave resistance;
18 percent to overcome skin friction;
17 percent to overcome resistance from the wake and propeller wash against the hull; and
3 percent to overcome air resistance.
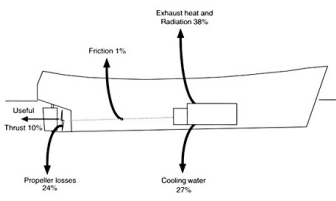
Only 10% of the energy is converted into thrust.
A turbo charger regains some of the exhaust energy.
Cleaning the forward quarter of the hull yields one-third of the benefit gained from treating the whole hull.
Cleaning the propeller alone will do the most to reduce fuel consumption.
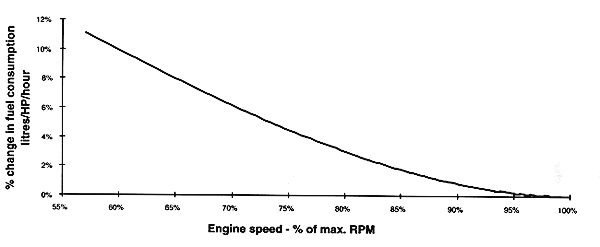
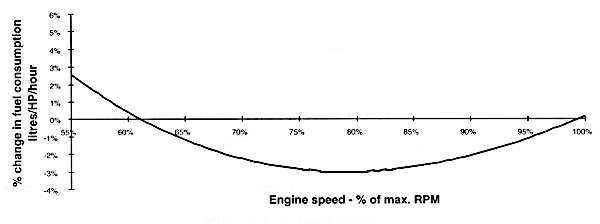
A normally aspirated diesel engine tends to use more fuel per horsepower of output at lower engine speed, and operate most efficiently at 100% RPM
The diameter of the propeller should be as large as the hull design and engine installation allow.
The larger the diameter of the propeller, the slower the shaft speed RPM that is required to absorb the same power. Therefore, for an efficient propeller, not only should the diameter be as large as possible but, as a result, the shaft speed needs to be slow.
The thickness of a propeller blade has little effect on efficiency, but it can be more prone to cavitation.
A large propeller boss; hub, reduces efficiency. A controllable pitch propeller is about 2 percent less efficient because of the boss. However a controllable-pitch propeller can result in fuel savings of up to 15 percent compared with a fixed-pitch propeller operating in a nozzle.
Clearances, three-bladed propeller- % of propeller diameter
Minimum clearance between tip and hull – 17%
Minimum clearance between tip and keel – 4%
Minimum distance from deadwood to propeller at 35% of propeller diameter – 27%
Maximum distance from propeller to rudder at 35% of propeller diameter – 10%
Maximum bare shaft length – 4x shaft diameter
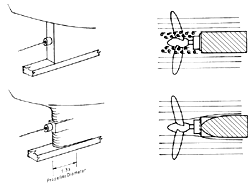
The rake; or angle of the prop blade toward the aft, has no direct effect on propeller efficiency. Rake is added so that larger blades can be used in the area available; aperture.
The distances between the propeller and the hull affect how efficiently the propeller operates within the flow of water around the hull, and the amount of vibration caused by the propeller.
The “deadwood” is an extension from the keel that passes under the prop in order to support the bottom of the rudder. The distance from the deadwood to the propeller should be large.
The distance from the propeller to the rudder should be kept small to maintain steering control.
In the design and installation of trawler propellers, the tip-to-hull clearance can be as little as 8 to 10 percent of propeller diameter.
The propeller may be incorrectly specified if:
* the engine fails to achieve designed RPM and is overloaded;
* the engine passes designed RPM at full throttle, over-revs and is underloaded;
* the propeller is overloaded and shows signs of cavitation and surface erosion.
The hull needs to be faired to allow for a smooth flow of water into the propeller.
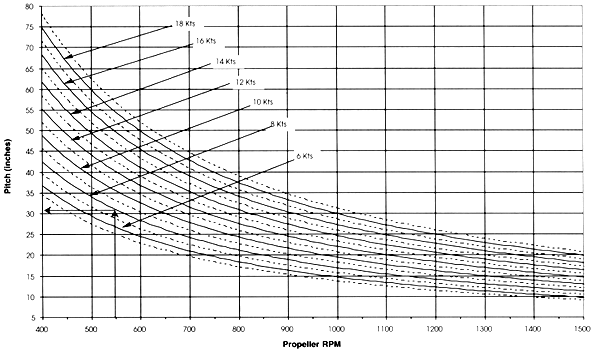
Prop Pitch – The Prop Pitch Chart should be read by entering along the horizontal axis at the RPM corresponding to the propeller’s operating RPM at cruising speed. A vertical line should then be drawn until intersecting the curve corresponding to the required cruising speed. From that point of intersection, a horizontal line is then drawn to the left-hand axis where the pitch can be read. It is very important that the required operating speed reflect the installed power and the type of vessel.
Read more about propellers at:
Making Sense of Diesel Engine Specs www.frontierpower.com/library/makingsense.htm
Fuel and Financial Savings for Operators of Small Fishing Vessels www.fao.org/docrep/x0487e/x0487e00.htm